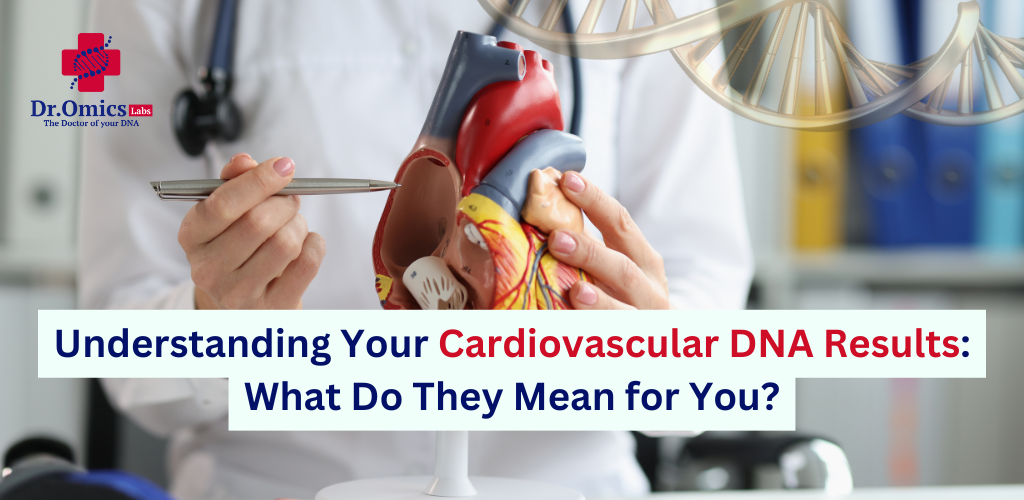
As personalized medicine advances, DNA testing has emerged as a powerful tool for assessing cardiovascular health risks. By analyzing your genetic blueprint, these tests offer valuable insights into your predisposition to various heart conditions, helping to create a clearer picture of individual health risks and enabling tailored preventive strategies.
However, interpreting cardiovascular DNA results can be challenging. These tests often reveal complex data about genetic variants linked to heart health, which can be overwhelming without proper guidance. This guide simplifies how to understand your results, explaining how specific genetic markers impact heart disease risk and outlining actionable steps you can take to leverage these insights for proactive heart health management.
Decoding Your Cardiovascular DNA Results
Cardiovascular DNA testing examines specific genetic variants, often single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), that influence your risk for heart disease. These genetic markers can affect cholesterol metabolism, blood pressure regulation, and inflammation, playing a critical role in cardiovascular health.
Key Genetic Markers Analyzed in Cardiovascular DNA Testing
LPA Gene
The LPA gene influences the levels of lipoprotein(a), or Lp(a), in the blood. High levels of Lp(a) are linked to an increased risk of atherosclerosis, where plaque builds up in arteries and restricts blood flow. Variants in this gene that raise Lp(a) levels are significant risk factors for coronary artery disease, especially for those with a family history of heart disease.(1)
APOE Gene
The APOE gene helps with fat metabolism, and its ε4 variant is associated with higher coronary artery disease risk. People with this variant, particularly those with high cholesterol, have an increased chance of LDL cholesterol accumulation, which can contribute to plaque buildup and heart disease.(2)
NOS3 Gene
The NOS3 gene is essential for nitric oxide production, which supports blood vessel health and regulates blood pressure. Variants in this gene can reduce nitric oxide levels, potentially leading to hypertension and vascular issues, both important factors in cardiovascular risk.(3)
ACE Gene
The ACE gene affects blood pressure through a polymorphism called the I/D variant. The “D” allele is associated with higher ACE activity, which may increase blood pressure and is linked to a higher risk of myocardial infarction, especially when combined with other risk factors.(4)
Interpreting Your DNA Test Results: What to Look For
Receiving your cardiovascular DNA test results can be overwhelming, but understanding the key sections of your report is crucial for taking informed actions. Here’s a breakdown of what your report might include:
- Genetic Risk Score:
- This score aggregates the impact of multiple genetic variants associated with cardiovascular disease. It provides an overall assessment of your genetic predisposition. A higher score indicates increased susceptibility but does not guarantee that you will develop heart disease.
- Gene-Specific Analysis:
- The report may highlight specific genes where your genetic results differ from the general population. For example, a variant in the CYP2C19 gene can affect your response to antiplatelet medications like clopidogrel, commonly prescribed after heart attacks.(5)
- Risk Factor Summary:
- This section correlates your genetic data with traditional cardiovascular risk factors like hypertension, dyslipidemia, and thrombosis. Your risk may be classified as low, moderate, or high for each condition based on your genetic profile.
The Importance of Genetic Counseling
Interpreting cardiovascular DNA test results requires specialized knowledge, which is where genetic counseling comes in. Genetic counselors can help you understand the implications of your test results, offering insights into your genetic predispositions and guiding you in making informed decisions for your health.
Benefits of Genetic Counseling:
- Personalized Risk Assessment:
- A genetic counselor can contextualize your genetic results within your broader health profile, considering factors like family history, lifestyle, and environmental influences.
- Clarification of Complex Results:
- Understanding the interplay between multiple genetic markers and traditional risk factors can be complex. Genetic counselors provide clarity, ensuring you accurately understand your risk profile.
Translating Genetic Insights into Lifestyle Modifications
While genetic predispositions play a significant role in cardiovascular health, lifestyle factors can either mitigate or exacerbate these risks. Understanding how your genes interact with your environment can help in optimizing lifestyle choices.
Examples of Lifestyle Considerations Based on Genetic Insights:
- Cholesterol Management:
- If your test shows a predisposition to high LDL levels due to APOB or PCSK9 variants, diet modifications focusing on reducing saturated fats and increasing fiber intake may be recommended.(6)
- Blood Pressure Control:
- Variants in the ACE or AGT genes may indicate a predisposition to hypertension. In this case, sodium intake might need to be monitored closely, alongside regular physical activity to manage blood pressure.(7)
- Inflammation Reduction:
- Genetic markers linked to inflammation may suggest a higher risk for cardiovascular events. Dietary adjustments to include anti-inflammatory foods could be beneficial.
Understanding the Role of DNA in Heart Disease Prevention
Cardiovascular DNA testing is not just about identifying risks—it also empowers individuals to take preventive measures. The knowledge gained from genetic testing can be used to craft personalized health strategies, integrating both genetic and lifestyle factors to optimize heart health.
By leveraging DNA insights, individuals can better understand their cardiovascular risk profile, allowing for early interventions and tailored health plans. However, it’s essential to combine these insights with regular medical check-ups and professional guidance to effectively manage heart health.
Conclusion
Cardiovascular DNA testing offers a unique window into your heart health, providing a deeper understanding of your genetic predispositions. By interpreting these results with the support of genetic counseling, you can make informed and proactive choices to reduce your risk of heart disease. As personalized medicine evolves, leveraging DNA insights becomes a powerful tool in preventive healthcare, empowering you to take control of your heart health and enhance your overall well-being. Embrace this cutting-edge approach to unlock a healthier future, where your genetic information guides your path to optimal cardiovascular health.
References:
(1)https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/ATV.0000000000000147
(2)https://www.eneuro.org/content/6/5/ENEURO.0267-19.2019
(3)https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6728140/
(4)https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9726265/
(5)https://openheart.bmj.com/content/10/2/e002436
(6)https://medlineplus.gov/howtolowercholesterolwithdiet.html
(7)https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0304271