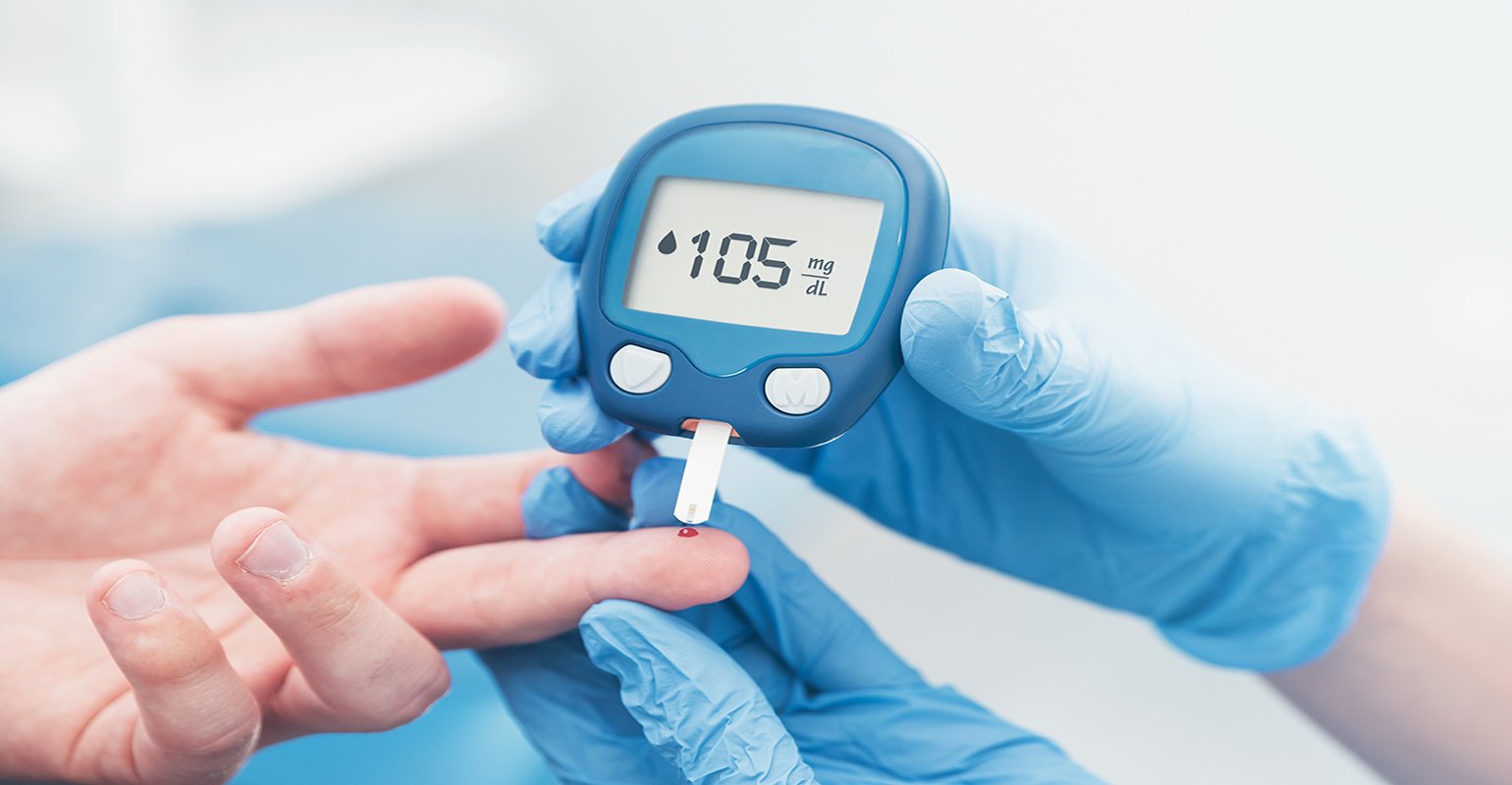
Diabetes diagnosis is a critical aspect of disease management, allowing for timely interventions to prevent complications and improve patient outcomes. Recent innovations in diagnostic techniques have revolutionised the detection and monitoring of diabetes, enhancing accuracy, efficiency, and patient convenience. This blog explores the latest advancements in diabetes diagnosis, highlighting novel technologies, emerging biomarkers, and their implications for clinical practice.
Innovations :
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) in Diabetes:
- Continuous glucose monitoring systems have emerged as a game-changer in diabetes management, providing real-time data on glucose levels throughout the day and night. These wearable devices offer insights into glucose fluctuations, trends, and patterns, enabling personalised treatment adjustments and proactive management of blood sugar levels. Continuous glucose monitoring enhances glycemic control, reduces the risk of hypoglycemia, and empowers patients to make informed decisions about their diabetes management.
Point-of-Care Testing in Diabetes:
- Point-of-care testing (POCT) facilitates rapid and convenient diabetes screening and monitoring in various healthcare settings, including clinics, pharmacies, and even home environments. Portable glucometers, haemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) analyzers, and urine glucose testing kits enable quick assessment of blood sugar levels, glycemic control, and diabetes risk. POCT enhances accessibility to diagnostic services, particularly in resource-limited settings, and supports timely interventions to prevent diabetes-related complications.
Advanced Imaging Modalities in Diabetes:
- Advanced imaging modalities, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT), and positron emission tomography (PET), offer valuable insights into the pathophysiology of diabetes and its associated complications. These non-invasive imaging techniques enable visualisation of pancreatic morphology, β-cell function, insulin resistance, and vascular changes, aiding in early detection, risk stratification, and treatment planning for individuals at risk of diabetes or its complications.
Biomarker Discovery in Diabetes:
- Recent advancements in biomarker discovery have identified novel molecules and pathways associated with diabetes development and progression. Blood-based biomarkers, such as circulating microRNAs, inflammatory markers, and metabolites, offer potential diagnostic and prognostic utility in diabetes risk assessment and monitoring. Moreover, emerging technologies, such as proteomics, metabolomics, and genomic profiling, facilitate comprehensive profiling of molecular signatures associated with diabetes, paving the way for precision medicine approaches in disease management.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning in Diabetes:
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms have transformed diabetes diagnosis and risk prediction by leveraging vast datasets and complex patterns in patient data. AI-powered diagnostic tools analyse clinical parameters, genetic information, lifestyle factors, and imaging findings to generate personalised risk scores, stratify individuals based on diabetes risk, and guide preventive interventions. These innovative approaches enhance diagnostic accuracy, enable early intervention, and support personalised diabetes management strategies.
How has technology improved diabetes management
Technology has significantly improved diabetes management through various innovations. These include continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), increasingly automated insulin pumps, connected insulin pens, and apps, all of which have been associated with improved clinical, psychosocial, and behavioral outcomes for people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes, especially those requiring intensive insulin therapy[1]. Diabetes technologies have shown to improve health outcomes, offering more precise treatments and increased glucose information, ultimately empowering individuals living with diabetes[2]. Recent advances in technology provide valuable means of improving the accuracy and safety of insulin therapy and simplifying glucose monitoring[3]. The use of technology and effective information management is considered an integral part of diabetes care, offering personalized approaches to meet individual needs[4]. These innovations not only improve patient outcomes but also require education and support for healthcare professionals and patients to effectively utilize these tools[1]. Therefore, the use of technology in diabetes management has the potential to significantly enhance patient care and quality of life[5].
What are some of the challenges in implementing new diabetes technologies
Implementing new diabetes technologies can present several challenges. One of the main challenges is the cost of these technologies, which can be a barrier to access for some patients[1]. Another challenge is the need for healthcare professionals and patients to be educated on how to use these devices effectively[1][2]. Patients may also face challenges in integrating these technologies into their daily lives, such as the need for frequent device maintenance and the inconvenience of carrying and using multiple devices[2]. Additionally, the use of technology in diabetes management requires careful consideration of privacy and security concerns, as well as the need for data management and analysis[3]. Finally, the rapid pace of technological advancements can make it difficult for healthcare professionals to keep up with the latest developments and determine which technologies are most appropriate for their patients[4]. Despite these challenges, the use of technology in diabetes management has the potential to significantly enhance patient care and quality of life[5].
Conclusion :
In conclusion, recent innovations in diabetes diagnosis, including continuous glucose monitoring, point-of-care testing, advanced imaging modalities, biomarker discovery, and artificial intelligence-driven diagnostic tools, have revolutionized diabetes care and management. These advancements offer enhanced accuracy, efficiency, and patient convenience, empowering individuals with diabetes to make informed decisions and achieve better glycemic control. However, implementing new diabetes technologies presents challenges related to cost, education, integration into daily life, privacy concerns, and keeping pace with rapid technological advancements. Despite these challenges, the potential of technology to improve patient outcomes and quality of life in diabetes management is substantial
Citations:
[4] https://www.jdrf.org/blog/?topic=the-power-of-us