In recent years, technological advancements have revolutionized prenatal screening tests, providing expectant parents with accurate and reliable information about their baby’s health. Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT) has emerged as a groundbreaking genetic screening option that offers unparalleled insight into an unborn child’s genetic makeup, helping identify potential chromosomal abnormalities. In this blog, we will delve into the details of NIPT testing, its significance, and its benefits.
What is NIPT Testing?
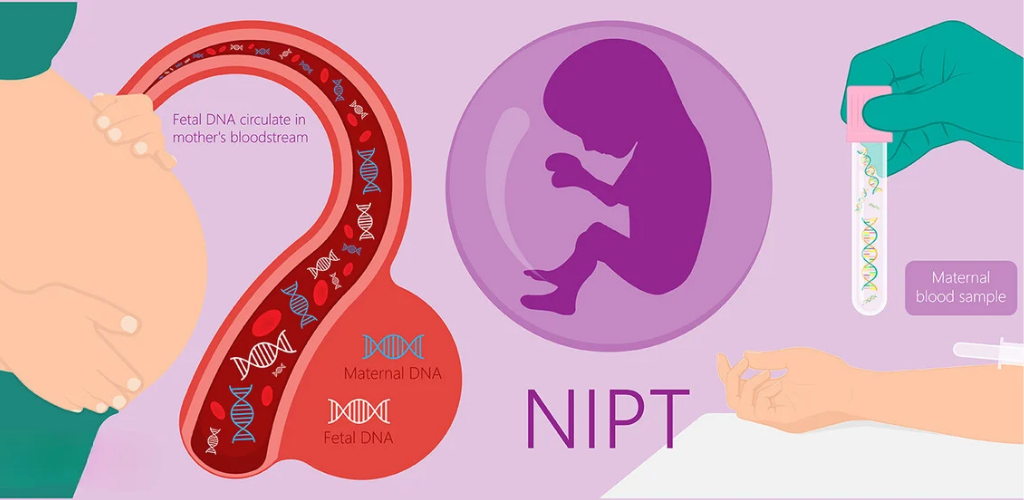
Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT) is a sophisticated screening method that analyzes cell-free fetal DNA (cffDNA) circulating in the mother’s blood during pregnancy. Unlike traditional invasive procedures like amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling, NIPT poses no risk to the mother or the fetus. By examining the fetal DNA present in the mother’s bloodstream, NIPT can identify the risk of chromosomal disorders with remarkable accuracy.
How Does NIPT Testing Work?
NIPT testing uses advanced technology to detect and analyze fetal DNA fragments in the maternal blood. It relies on the principle that during pregnancy, a small fraction of the placental DNA enters the mother’s bloodstream. By isolating these fetal fragments, the lab can then sequence and analyze the DNA to identify any chromosomal abnormalities. The most common conditions screened for include Down syndrome (trisomy 21), Edwards syndrome (trisomy 18), and Patau syndrome (trisomy 13).
When is NIPT Testing Recommended?
NIPT testing is generally recommended for women considered to be at higher risk of having a baby with a chromosomal abnormality. This includes women who are 35 years or older, those with a previous pregnancy affected by a chromosomal disorder, and those with a family history of genetic conditions. However, nowadays, NIPT is increasingly offered to all pregnant women due to its high accuracy and non-invasive nature.
Benefits of NIPT Testing:
- Accuracy: NIPT has an impressive accuracy rate, often providing a detection rate of over 99% for common chromosomal abnormalities.
- Early Detection: NIPT can be performed as early as 10 weeks into pregnancy, allowing parents to learn about potential genetic conditions at an earlier stage.
- Non-Invasive: Since NIPT only requires a blood sample from the mother, it poses no risk of complications such as miscarriage compared to invasive procedures.
- Reduced Need for Further Testing: A positive NIPT result can be followed up with confirmatory testing, such as amniocentesis, to establish a definitive diagnosis.
Limitations of NIPT Testing:
- False Positives and False Negatives: While NIPT is highly accurate, it can occasionally yield false positive or false negative results. Further diagnostic testing is often required to confirm or rule out any potential abnormalities.
- It Does Not Screen for All Genetic Conditions: NIPT primarily focuses on common chromosomal disorders, like trisomy 21, 18, and 13. It may not detect other genetic conditions or structural abnormalities.
The Importance of Genetic Counseling:
Before undergoing NIPT testing, it is essential for expectant parents to receive comprehensive genetic counseling. Genetic counselors can help explain the options, limitations, and potential results of NIPT testing. They play a crucial role in facilitating informed decision-making for the best interest of the parents and their unborn child.
Conclusion:
Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT) has revolutionized prenatal screening, providing expectant parents with accurate and early information about potential genetic conditions in their unborn child. With its high accuracy and minimal risk, NIPT testing has become a valuable tool in prenatal care. By understanding its benefits, limitations, and the importance of genetic counseling, parents can make informed decisions to promote the health and well-being of both themselves and their baby.