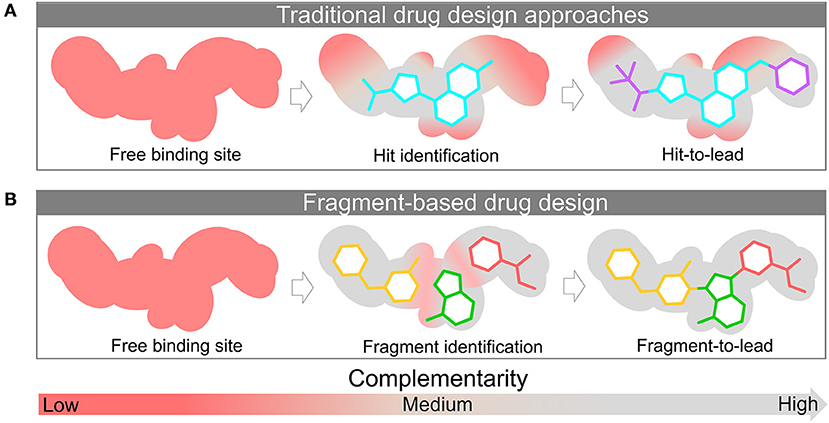
Hit identification is the process of finding small molecules, also called hits, that can bind to a biological target and modify its function. It is the first committed step in a successful drug discovery project, and it can influence the outcome of the subsequent stages, such as hit-to-lead and lead optimization. Therefore, it is important to design and implement a robust and effective hit identification strategy that can deliver high-quality hits with the desired properties and characteristics.
What are the main approaches to hit identification?
There are two main approaches to hit identification: target-based and phenotypic. Target-based hit identification involves screening a large and diverse library of compounds against a known and validated target, using various biochemical or biophysical assays. Phenotypic hit identification involves screening compounds against a disease-relevant phenotype, such as a cell or tissue model, without knowing the molecular target. Both approaches have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of the best one depends on the nature of the target, the disease, and the available resources.
How to design and execute a hit identification campaign?
A successful hit identification campaign requires careful planning and execution, involving several steps and factors. Some of the key steps and factors are:
- Defining the target and the disease of interest, and the criteria for hit selection and prioritization
- Developing and validating suitable assays that can measure the activity and specificity of the compounds
- Selecting the appropriate screening method and technology, such as high-throughput screening, fragment-based screening, or virtual screening
- Choosing the optimal compound library, based on the diversity, quality, and availability of the compounds
- Performing the screening and analyzing the data, using various statistical and computational tools
- Confirming and characterizing the hits, using orthogonal assays and filters
- Evaluating the potential and feasibility of the hit series for further optimization and development
What are the challenges and opportunities in hit identification?
Hit identification is a challenging and complex process, involving many uncertainties and risks. Some of the common challenges are:
- Finding hits that are not only active, but also selective, drug-like, and tractable
- Dealing with false positives and false negatives, and minimizing the attrition rate
- Balancing the speed, cost, and quality of the screening
- Integrating the data and knowledge from different sources and disciplines
- Adapting to the evolving and emerging targets and diseases
However, hit identification also offers many opportunities and benefits, such as:
- Discovering novel and innovative compounds and mechanisms of action
- Expanding the chemical and biological space and diversity
- Enabling the translation of basic research into clinical applications
- Accelerating the drug discovery pipeline and improving the success rate
- Contributing to the advancement of science and medicine
Conclusion
Hit identification is a vital and challenging step in drug discovery, and it can determine the fate of a drug discovery project. By applying the best practices and strategies, and leveraging the latest technologies and tools, it is possible to identify high-quality hits that can lead to the development of effective and safe drugs for various diseases.
References
- Foley, T. L., Burchett, W., Chen, Q., Flanagan, M. E., Kapinos, B., Li, X., … & Peakman, M. C. (2021). Selecting Approaches for Hit Identification and Increasing Options by Building the Efficient Discovery of Actionable Chemical Matter from DNA-Encoded Libraries. SLAS Discovery, 26(2), 263-280.
- Kontoyianni, M. (2017). Docking and virtual screening in drug discovery. In Proteomics for Drug Discovery (pp. 263-280). Humana Press, New York, NY.
- Niesen, F. H., Berglund, H., & Vedadi, M. (2007). The use of differential scanning fluorimetry to detect ligand interactions that promote protein stability. Nature protocols, 2(9), 2212-2221.
- Lo, M. C., Aulabaugh, A., Jin, G., Cowling, R., Bard, J., Malamas, M., & Ellestad, G. (2004). Evaluation of fluorescence-based thermal shift assays for hit identification in drug discovery. Analytical biochemistry, 332(1), 153-159.