Atherosclerosis is a serious cardiovascular disease that requires immediate attention. We will look at the symptoms, causes, preventative tactics, and successful treatment choices for atherosclerosis in this complete guide. Let’s go through the complexities of this health issue together.
What is Atherosclerosis
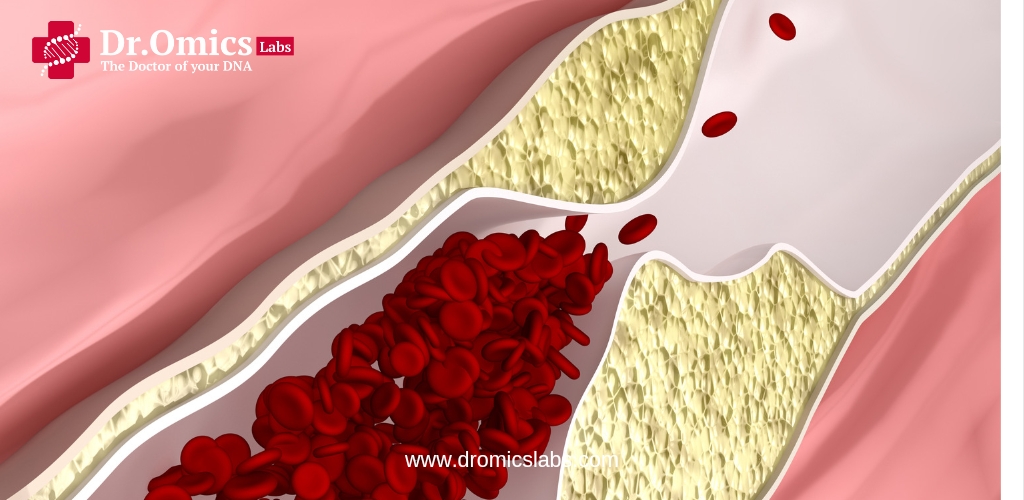
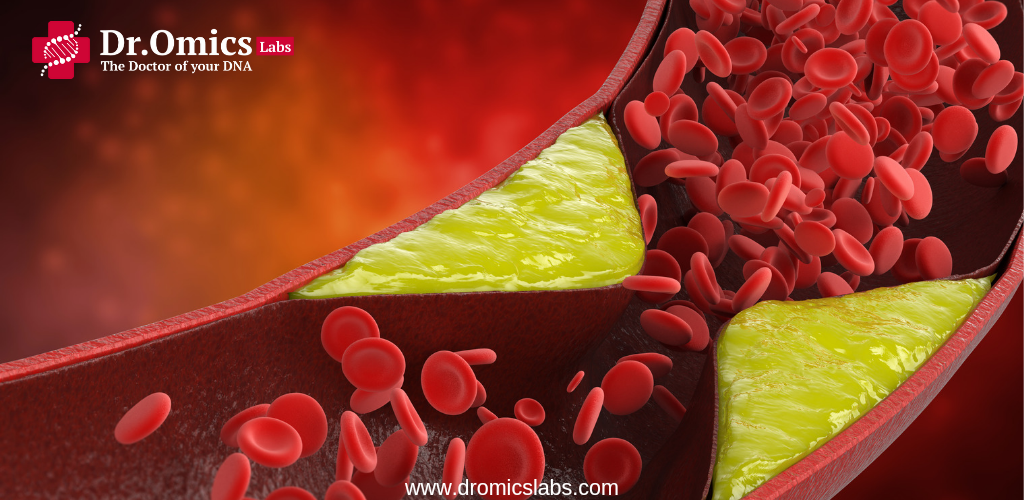
Atherosclerosis is a cardiovascular disease, a condition characterized by the buildup of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances in the arteries. This results in plaque formation in the walls of the arteries, which narrows the arteries. These narrow arteries can restrict blood flow, due to which oxygen and nutrients do not reach the tissues properly.
You can also read – Atherosclerosis – A Two Minute Read
Formation of Plaque
Plaque, also called atherosclerotic plaque, is a combination of cholesterol, fat, calcium, and other substances. When plaque grows, the walls of the arteries thicken, and this gradually restricts blood flow. The effect of this condition can occur in any part of the body, depending on the location of the affected arteries.
Causes of Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a complex process influenced by various factors.
Here are the key causes of atherosclerosis:
- High Cholesterol: Elevated levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, often referred to as “bad” cholesterol, contribute to the formation of plaque in the arteries.
- Hypertension (High Blood Pressure): High blood pressure puts excessive force on the arterial walls, making them more susceptible to damage. In response to this damage, the body initiates the process of atherosclerosis.
- Smoking: Tobacco smoke contains harmful chemicals that can damage blood vessels and accelerate the accumulation of plaque. Smoking also reduces the effectiveness of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, known as “good” cholesterol.
- Diabetes: Individuals with diabetes have an increased risk of atherosclerosis. High blood sugar levels can damage the lining of arteries, promoting the buildup of plaque.
- Inflammation: Chronic inflammation, often associated with conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus, can contribute to the development of atherosclerosis.
- Genetics and Family History: A family history of atherosclerosis or cardiovascular diseases can increase an individual’s susceptibility. Genetic factors may influence cholesterol levels and the body’s response to arterial damage.
- Age and Gender: Aging is a natural risk factor for atherosclerosis. Men generally face a higher risk than premenopausal women, but after menopause, the risk for women increases.
- Obesity and Unhealthy Diet: Being overweight or obese, particularly when combined with an unhealthy diet high in saturated and trans fats, can contribute to high cholesterol levels and arterial damage.
- Lack of Physical Activity: Sedentary lifestyles contribute to various cardiovascular risk factors, including obesity, hypertension, and high cholesterol, all of which play a role in atherosclerosis.
- Stress: Chronic stress may contribute to atherosclerosis through mechanisms like increased blood pressure and unhealthy coping behaviors such as overeating or smoking.
- Autoimmune Conditions: Certain autoimmune diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus, may increase inflammation and contribute to atherosclerosis.
Understanding these causes is crucial for prevention. Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding tobacco, can significantly reduce the risk of developing atherosclerosis. Additionally, managing conditions like diabetes and hypertension is essential for overall cardiovascular health. Regular medical check-ups can help monitor and address these risk factors proactively.
Symptoms of Atherosclerosis
Symptoms of atherosclerosis often depend on the specific arteries affected and the extent of the blockage. Common symptoms of atherosclerosis include:
- Chest Pain or Angina : Reduced blood flow to the heart muscle may result in chest pain or discomfort, known as angina. This discomfort can extend to the arms, neck, jaw, shoulder, or back.
- Shortness of Breath : Atherosclerosis in the arteries supplying blood to the heart can lead to shortness of breath, especially during physical exertion.
- Fatigue : Decreased blood flow may cause fatigue and a general feeling of weakness, impacting overall energy levels.
- Leg Pain or Numbness : Atherosclerosis affecting the arteries in the legs can lead to pain, numbness, or weakness in the thighs, calves, and feet, a condition known as peripheral artery disease (PAD).
- Slurred Speech or Weakness : If atherosclerosis affects the arteries supplying blood to the brain, it can result in stroke-like symptoms such as slurred speech, weakness, or paralysis on one side of the body.
- Erectile Dysfunction : Reduced blood flow to the genital area may contribute to erectile dysfunction in men.
Prevention of Atherosclerosis
Preventing atherosclerosis involves adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle and managing risk factors.
Here are key strategies for preventing atherosclerosis:
- Maintain a Healthy Diet:
- Emphasize a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Limit saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium intake.
- Choose heart-healthy fats like those found in olive oil, avocados, and nuts.
- Regular Physical Activity:
- Engage in regular aerobic exercise, such as brisk walking, jogging, or cycling.
- Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for atherosclerosis. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce the risk of developing this condition.
- Manage Blood Pressure:
- Monitor blood pressure regularly and work with healthcare professionals to keep it within a healthy range.
- Adopt lifestyle changes, including a low-sodium diet and regular exercise, to help manage blood pressure.
- Control Cholesterol Levels: Maintain healthy cholesterol levels by adopting a diet low in saturated and trans fats.
- Manage Diabetes:
- If you have diabetes, work closely with healthcare providers to manage blood sugar levels effectively.
- Adopt a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight:
- Achieve and maintain a healthy weight through a combination of a balanced diet and regular physical activity.
- Obesity is a significant risk factor for atherosclerosis.
- Stress Management:
- Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing, or hobbies.
- Chronic stress can contribute to the development of atherosclerosis.
- Limit Alcohol Intake: If you choose to drink alcohol, do so in moderation. Limit alcohol consumption to one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men.
- Regular Health Check-ups:
- Schedule regular check-ups with healthcare providers to monitor blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and overall cardiovascular health.
- Early detection and management of risk factors are crucial for prevention.
- Medication Adherence:
- If prescribed medications for conditions like hypertension or high cholesterol, adhere to the recommended treatment plan.
- Follow up with healthcare providers to monitor the effectiveness of medications.
- Genetic Counselling: If there is a family history of atherosclerosis or cardiovascular diseases, consider genetic counselling to understand potential risks and preventive measures.
Adopting these preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of atherosclerosis and promote overall cardiovascular health. It’s essential to personalize these strategies based on individual health conditions and consult with healthcare professionals for personalized guidance.
Treatments of Atherosclerosis
The treatment of atherosclerosis typically involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medications, and, in some cases, medical procedures. Here are the main components of treating atherosclerosis:
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Healthy Diet: Adopt a diet that is low in saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium. Emphasize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to improve cardiovascular health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week.
- Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking is crucial for managing atherosclerosis. Smoking cessation programs and support can be beneficial.
- Medications:
- Statins: These medications lower cholesterol levels and may reduce the progression of atherosclerosis.
- Antiplatelet Drugs: Aspirin or other antiplatelet medications may be prescribed to reduce the risk of blood clot formation.
- Blood Pressure Medications: If blood pressure is elevated, medications to control blood pressure may be prescribed.
- Anticoagulants: In some cases, anticoagulant medications may be recommended to prevent blood clots.
- Interventional Procedures:
- Angioplasty and Stent Placement: In this procedure, a catheter with a balloon is used to open a narrowed artery, and a stent may be placed to keep the artery open.
- Atherectomy: This involves removing plaque from the arteries using specialized devices.
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): In severe cases, bypass surgery may be performed to reroute blood flow around blocked arteries.
- Cardiac Rehabilitation: A structured program involving exercise, education, and support for individuals with cardiovascular diseases. It helps in improving overall heart health and managing risk factors.
- Monitoring and Follow-up:
- Regular check-ups and monitoring of blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and other cardiovascular risk factors are essential.
- Adjustments to the treatment plan may be made based on the individual’s response to medications and lifestyle changes.
- Management of Coexisting Conditions: Effective management of conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and other cardiovascular risk factors is crucial for overall treatment success.
- Genetic Counselling: Consider genetic counselling if there is a family history of atherosclerosis or cardiovascular diseases. Genetic counselors can assess the risk of hereditary factors contributing to atherosclerosis and provide information on preventive measures.
Note: Dr.Omics Labs offers genetic counselling services to help you understand your genetic predisposition to conditions like atherosclerosis. Our experts can guide you through the assessment of hereditary factors and provide valuable insights to monitor and improve your overall health.
It’s important to note that the treatment plan for atherosclerosis is often individualized based on the severity of the condition, the presence of other health issues, and the individual’s overall health. Consultation with a healthcare professional is essential to determine the most appropriate and effective treatment approach for each person.
Take every illness seriously. With the aim of increasing awareness, we have written this blog to inform you about the disease atherosclerosis, its prevention, and its treatment. We have written many health-related blogs, and we will continue to do so, but our main goal is to keep you alert about your health. Dr. Omics Labs, through genetic studies, can provide early insights into potential diseases.
Contact us today. Let’s work together to make our country disease-free.